What is AR, VR, XR, and VR? A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered about the differences between Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Extended Reality (XR), and VR? These technologies are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct characteristics and applications. Let’s dive into a detailed comparison to help you understand the nuances of each.
Augmented Reality (AR)

Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world. It enhances the user’s perception of reality by adding virtual elements to their view. AR can be experienced through smartphones, tablets, or specialized AR glasses.
Here are some key features of AR:
- Overlay of digital information: AR adds virtual objects, text, or images to the real world, allowing users to interact with them.
- Real-time interaction: AR applications can provide real-time information and updates, making them useful for navigation, education, and entertainment.
- Location-based services: Many AR applications use GPS or indoor positioning systems to provide location-based information.
Some popular AR applications include:
- Snapchat: Known for its filters and lenses that overlay digital effects onto the real world.
- Google Maps: Offers AR navigation features that help users find their way in unfamiliar locations.
- Headspace: Uses AR to guide users through meditation and mindfulness exercises.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual Reality (VR) is a technology that creates a completely immersive experience, transporting users to a virtual world. VR headsets block out the real world and replace it with a simulated environment. Users can interact with this virtual world through controllers, motion sensors, or even their own movements.
Here are some key features of VR:
- Immersive experience: VR creates a sense of presence, making users feel like they are part of the virtual world.
- Full-body tracking: Some VR systems can track the user’s entire body, allowing for more natural and intuitive interactions.
- High-quality visuals and sound: VR headsets provide high-resolution visuals and surround sound to enhance the immersive experience.
Some popular VR applications include:
- Beat Saber: A rhythm game that uses VR controllers to slice virtual blocks to the beat of music.
- The Lab: An educational VR game that teaches users about various scientific concepts.
- Half-Life Alyx: A VR game that offers an immersive first-person shooter experience.
Extended Reality (XR)
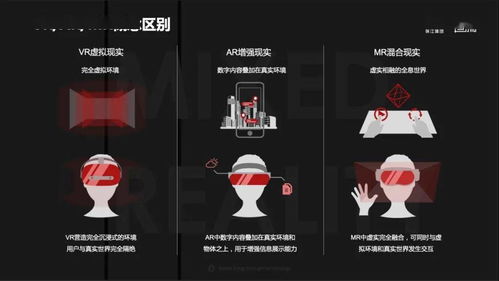
Extended Reality (XR) is an umbrella term that encompasses both AR and VR, as well as other related technologies. XR refers to any technology that extends or enhances the real world with digital information. This includes not only AR and VR but also Mixed Reality (MR), which combines elements of both AR and VR.
Here are some key features of XR:
- Combination of AR and VR: XR technologies can use both AR and VR to create a more comprehensive and interactive experience.
- Real-time interaction: Like AR, XR applications can provide real-time information and updates.
- Location-based services: XR can also leverage location-based services to enhance the user experience.
Some popular XR applications include:
- Microsoft HoloLens: A mixed reality headset that allows users to interact with both the real and virtual worlds.
- Magic Leap One: Another mixed reality headset that provides an immersive experience with real-time interaction.
- Facebook Horizon Workrooms: A virtual workspace that allows users to collaborate and communicate in a virtual environment.
VR vs. AR vs. XR: A Comparison Table
| Technology | Immersive Experience | Real-time Interaction | Location-based Services |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|






