AR Stands for Medical: A Comprehensive Overview
Augmented Reality (AR) has been making waves across various industries, and the medical field is no exception. With its ability to overlay digital information onto the real world, AR has the potential to revolutionize healthcare. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of AR in medicine, exploring its applications, benefits, and challenges.
Applications of AR in Medicine
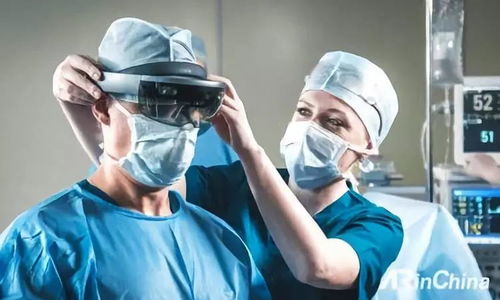
One of the most significant applications of AR in medicine is in surgical procedures. Surgeons can use AR to visualize complex anatomical structures and plan surgeries with greater precision. This technology can also be used to guide surgeons during operations, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
AR is also being used in medical education. Students can use AR to visualize human anatomy in 3D, making it easier to understand complex concepts. This interactive learning experience can enhance retention and comprehension, preparing future healthcare professionals for real-world challenges.
Benefits of AR in Medicine
One of the primary benefits of AR in medicine is improved patient care. By providing real-time information and guidance, AR can help healthcare professionals make more informed decisions, leading to better patient outcomes. Additionally, AR can reduce the need for invasive procedures, minimizing patient discomfort and recovery time.
AR can also enhance the efficiency of medical training. By providing a hands-on, interactive learning experience, AR can help medical students and professionals develop their skills more effectively. This can lead to a more skilled and confident workforce, ultimately benefiting patients.
Challenges of AR in Medicine

While AR has the potential to transform medicine, there are several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the cost of implementing AR technology. High-quality AR devices and software can be expensive, making it difficult for some healthcare facilities to adopt this technology.
Another challenge is the need for training and education. Healthcare professionals must be trained to use AR technology effectively, which requires time and resources. Additionally, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of AR data is crucial, as incorrect information can have serious consequences.
AR in Remote Healthcare
AR can also play a significant role in remote healthcare. By providing real-time assistance to healthcare professionals in remote areas, AR can help bridge the gap in healthcare access. This technology can be particularly beneficial in rural or underserved regions, where access to specialized care is limited.
AR can be used to provide remote consultations, allowing healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat patients without being physically present. This can improve patient outcomes and reduce the need for travel, saving time and resources.
AR in Medical Research
AR is not limited to clinical applications; it also has the potential to advance medical research. By providing researchers with a more immersive and interactive experience, AR can help them explore complex data and visualize biological processes more effectively.
AR can also facilitate collaboration among researchers, allowing them to share and discuss their findings in real-time. This can accelerate the pace of medical research and lead to new discoveries and treatments.
Conclusion
AR stands for Medical, and its potential to transform healthcare is immense. From improving patient care and medical training to advancing medical research, AR has the power to revolutionize the way we approach healthcare. While challenges remain, the benefits of AR in medicine are clear, and with continued innovation and investment, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the future.






