AR, VR, and MR: A Comprehensive Guide to Immersive Technologies
Immersive technologies have revolutionized the way we interact with digital content. Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are three distinct yet interconnected fields that offer unique experiences. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of each technology, exploring their features, applications, and the future of these groundbreaking advancements.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?

Augmented Reality (AR) is a technology that overlays digital information onto the real world. By using a smartphone, tablet, or AR glasses, users can see and interact with both the physical and digital environments simultaneously. AR enhances the real world by adding layers of digital content, such as images, videos, and 3D models.
One of the most popular applications of AR is in mobile gaming. Games like Pok茅mon Go have captivated millions of players worldwide, allowing them to catch virtual creatures in the real world. AR is also widely used in retail, where it helps customers visualize products in their own homes before making a purchase.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?

Virtual Reality (VR) is a fully immersive experience that transports users to a completely artificial environment. By wearing a VR headset, users can explore virtual worlds, interact with digital objects, and even communicate with other users in real-time. VR creates a sense of presence, making users feel as if they are truly inside the virtual environment.
The gaming industry has been a significant driver of VR adoption. Titles like Beat Saber and Half-Life: Alyx have pushed the boundaries of VR gaming, offering immersive experiences that are difficult to replicate in the real world. VR is also gaining traction in healthcare, where it is used for pain management, phobia treatment, and even surgical training.
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?
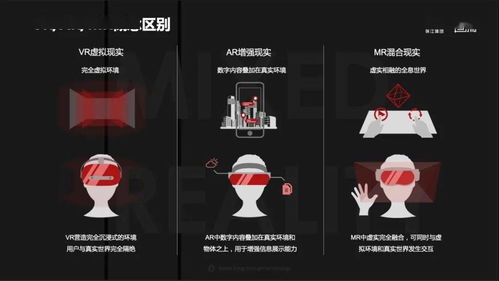
Mixed Reality (MR) combines the elements of AR and VR, creating a seamless blend of the physical and digital worlds. MR allows users to interact with both real-world objects and digital content simultaneously. Unlike AR, which overlays digital information onto the real world, MR integrates digital content into the physical environment.
One of the most notable applications of MR is in the automotive industry. Ford, for example, uses MR to help designers visualize and modify car interiors in real-time. MR is also being explored in education, where it can provide interactive and immersive learning experiences.
Table: Comparison of AR, VR, and MR
| Technology | Definition | Applications | Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Augmented Reality (AR) | Overlays digital information onto the real world | Mobile gaming, retail, education | Smartphones, tablets, AR glasses |
| Virtual Reality (VR) | Immerses users in a completely artificial environment | Gaming, healthcare, training | VR headsets, controllers |
| Mixed Reality (MR) | Combines elements of AR and VR | Automotive, education, design | MR headsets, controllers |
Challenges and Future of Immersive Technologies
While AR, VR, and MR offer exciting possibilities, there are several challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the cost of equipment. High-quality VR and AR headsets can be expensive, limiting access to these technologies for many users.
Another challenge is the development of content. Creating immersive experiences requires specialized skills and tools, which can be time-consuming and expensive. However, as the technology becomes more accessible, we can expect to see a surge in the creation of new and innovative content.
The future of immersive technologies looks promising. As hardware becomes more affordable and content continues to evolve, we can expect to see these technologies integrated into various aspects of our lives. From education to healthcare, immersive technologies have the potential to transform the way we interact with the world around us.
In conclusion, AR, VR, and MR are three powerful and interconnected technologies that offer unique experiences. By understanding their features, applications, and challenges, we can better appreciate the potential of these groundbreaking advancements.






