Understanding the Past Tense in Spanish: A Detailed Guide for You
Learning a new language can be an exciting journey, and Spanish, with its rich history and vibrant culture, is a popular choice for many language learners. One of the key aspects of mastering Spanish is understanding and using the past tense correctly. In this article, I will delve into the different past tenses in Spanish and provide you with a comprehensive guide to help you master them.
What is the Past Tense?

The past tense is a verb form that describes actions that have already been completed. In Spanish, there are several past tenses, each with its own specific use and rules. Understanding these tenses is crucial for effective communication in Spanish.
Simple Past (Pret茅rito Indefinido)
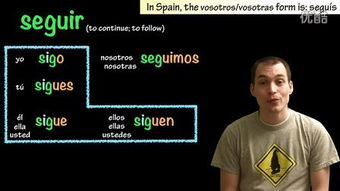
The simple past, known as “pret茅rito indefinido” in Spanish, is used to describe actions that were completed at a specific time in the past. It is the most common past tense and can be formed by adding the appropriate endings to the base form of the verb.
| Subject | Verb (Base Form) | Past Tense (Pret茅rito Indefinido) |
|---|---|---|
| Yo | comer | com铆 |
| T煤 | comer | comiste |
| 脡l/Ella/Se | comer | comi贸 |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | comer | comimos |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | comer | comisteis |
| Ellos/Ellas/Se | comer | comieron |
For regular verbs, the endings are -茅, -aste, -贸, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron. For irregular verbs, the endings can vary, and it is essential to memorize the specific endings for each verb.
Imperfect Past (Pret茅rito Imperfecto)

The imperfect past, known as “pret茅rito imperfecto,” is used to describe actions that were ongoing or habitual in the past. It is often used to talk about past events that were not completed or that occurred over a period of time.
For regular verbs, the endings are -aba, -abas, -aba, -谩bamos, -abais, and -aban. For irregular verbs, the endings can vary, and it is important to memorize the specific endings for each verb.
Pluperfect (Pret茅rito Pleno)
The pluperfect, known as “pret茅rito pleno,” is used to describe actions that were completed before another past action. It is often used to talk about past events that happened before another past event.
For regular verbs, the endings are -铆a, -铆as, -铆a, -铆amos, -铆ais, and -铆an. For irregular verbs, the endings can vary, and it is crucial to memorize the specific endings for each verb.
Present Perfect (Pret茅rito Perfecto)
The present perfect, known as “pret茅rito perfecto,” is used to describe actions that started in the past and continue to the present or that have a present result. It is often used to talk about recent past events or past events with a present connection.
For regular verbs, the endings are -茅, -iste, -贸, -imos, -isteis, and -ieron. For irregular verbs, the endings can vary, and it is essential to memorize the specific endings for each verb.
Practice and Conclusion
Mastering the past tenses in Spanish requires practice and dedication. By familiarizing yourself with the rules and endings for each tense, and by practicing with examples and exercises, you will be well on your way to becoming proficient in Spanish.
Remember, language learning








