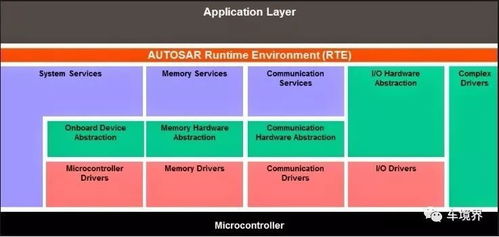
What is an AR Cycle?
Augmented Reality (AR) cycles are a fascinating blend of technology and creativity, offering users an immersive experience that overlays digital content onto the real world. In this detailed exploration, we’ll delve into the various aspects of AR cycles, from their history to their applications and the technology behind them.
History of AR Cycles
The concept of AR cycles can be traced back to the early 20th century, with the invention of the first head-mounted display (HMD) by Hans Jenny in 1929. However, it wasn’t until the late 20th century that AR technology began to gain traction, with the development of virtual reality (VR) systems and the introduction of AR-specific devices.
One of the key milestones in the history of AR cycles was the release of the ARKit and ARCore frameworks by Apple and Google, respectively, in 2017. These frameworks enabled developers to create AR experiences on a wide range of devices, including smartphones and tablets, making AR cycles more accessible to the general public.
How AR Cycles Work
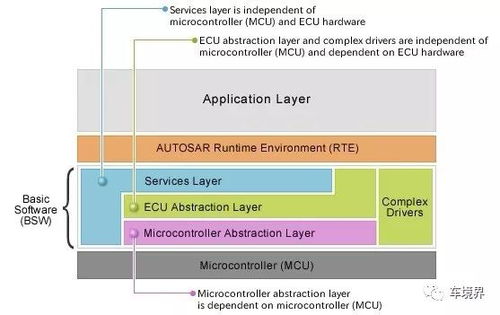
AR cycles work by using a combination of sensors, cameras, and software algorithms to overlay digital content onto the real world. Here’s a breakdown of the key components involved:
- Sensors: These devices, such as accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers, provide information about the device’s orientation and movement in space.
- Cameras: The device’s camera captures images of the real world, which are then processed by the software to determine the device’s position and orientation.
- Software Algorithms: These algorithms analyze the camera images and sensor data to create a 3D model of the real world, which is then used to overlay digital content onto the scene.
One of the most popular AR cycle applications is the use of AR filters on smartphones. These filters use the camera and sensors to detect the user’s face or environment and apply digital effects, such as masks, filters, and augmented objects.
Applications of AR Cycles

AR cycles have a wide range of applications across various industries. Here are some of the most notable examples:
- Entertainment: AR cycles are used in video games, movies, and live events to create immersive experiences that blend the real world with digital content.
- Education: AR cycles can be used to create interactive learning experiences, allowing students to visualize complex concepts and explore virtual environments.
- Real Estate: AR cycles can be used to provide virtual tours of properties, allowing potential buyers to see how a space would look with different furniture or decorations.
- Healthcare: AR cycles can be used to assist surgeons during operations, provide real-time information to patients, and train medical professionals.
Technology Behind AR Cycles
The technology behind AR cycles is complex and involves a variety of components. Here’s a closer look at some of the key technologies:
- Computer Vision: This field of study focuses on enabling computers to interpret and understand visual information from the real world.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning algorithms are used to analyze data and make predictions, which can be used to improve the accuracy of AR cycles.
- Graphics Processing: Graphics processing units (GPUs) are used to render the digital content and overlay it onto the real world in real-time.
One of the most important aspects of AR cycle technology is the ability to create a seamless and immersive experience. This requires high-quality graphics, accurate tracking, and real-time processing.
Future of AR Cycles
The future of AR cycles looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and new applications emerging. Some of the key trends include:
- Improved Hardware: As hardware becomes more advanced, AR cycles will become more powerful and capable of delivering more immersive experiences.
- Better Software: Advances in software will make AR cycles more intuitive and user-friendly, allowing a wider audience to enjoy the technology.
- New Applications: As AR cycles become more accessible, new applications will emerge in various industries, from entertainment to healthcare.
In conclusion, AR cycles are a powerful and versatile technology that has the potential to transform the way we interact with the world. By understanding








