Abbreviation AR: A Comprehensive Overview
Abbreviation AR, which stands for Augmented Reality, has become a buzzword in the tech industry over the past few years. It refers to the integration of digital information into the user’s perception of the real world. This article delves into the various aspects of AR, including its history, applications, technology, and future prospects.
History of Augmented Reality
The concept of AR dates back to the 1960s when a computer scientist named Ivan Sutherland developed the first AR system. However, it wasn’t until the 1990s that AR started gaining attention with the development of head-mounted displays (HMDs). Over the years, advancements in technology have made AR more accessible and practical for various applications.
Applications of Augmented Reality
AR has found its way into numerous industries, offering innovative solutions and enhancing user experiences. Here are some of the key applications of AR:
-
Healthcare: AR is used for medical training, patient care, and diagnostics. Surgeons can practice complex procedures using AR simulations, and patients can visualize their conditions and treatment options in a more interactive manner.
-
Education: AR provides immersive learning experiences, allowing students to explore historical sites, understand complex concepts, and engage with interactive content.
-
Real Estate: AR enables potential buyers to visualize properties and make informed decisions without physically visiting them. This technology is particularly useful for showcasing architectural designs and interior layouts.
-
Retail: AR enhances the shopping experience by allowing customers to try on clothes, visualize furniture in their homes, and compare products in real-time.
-
Entertainment: AR games and apps have gained immense popularity, offering immersive experiences and interactive storytelling.
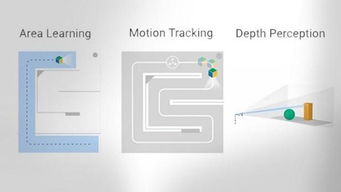
Technology Behind Augmented Reality
AR technology relies on several key components to create an immersive experience:
-
Camera: The camera captures the real-world environment and provides input to the AR system.
-
Display: The display presents the augmented content to the user, often through a smartphone, tablet, or HMD.
-
Processor: The processor analyzes the camera input and generates the augmented content in real-time.
-
Software: AR software algorithms enable the tracking of the real-world environment and the overlay of digital content.
One of the most crucial aspects of AR technology is the use of computer vision algorithms. These algorithms enable the system to recognize and track objects in the real world, allowing for accurate placement of augmented content.
Future Prospects of Augmented Reality
The future of AR looks promising, with several trends shaping its development:
-
Wearable Technology: As wearable devices become more advanced, AR will become more seamlessly integrated into our daily lives.
-
5G Connectivity: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable AR experiences, reducing latency and improving real-time interactions.
-
Cross-Platform Integration: AR will continue to be integrated with other technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI), creating more comprehensive and immersive experiences.
As AR technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications and a broader adoption across various industries.
Table: Key Advantages of Augmented Reality
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Immersive Experience | AR provides an immersive experience by overlaying digital content on the real world, allowing users to interact with both simultaneously. |
| Interactive Learning | AR can be used for interactive learning, enabling students to explore and understand complex concepts in a more engaging manner. |
| Enhanced Visualization | AR allows users to visualize objects and concepts in a more realistic and interactive way, making it easier to understand and remember information. |
| Improved Accessibility | AR can be used to make information and services more accessible to people with
|







